Heart failure is a serious condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to fatigue, fluid retention, shortness of breath, and other debilitating symptoms. If you’ve been diagnosed with heart failure, you may have been informed that a Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) pacemaker could be beneficial for your condition. But what exactly is a CRT pacemaker, and how could it help with heart failure? In this blog post, we will dive deep into CRT pacemakers, their role in heart failure treatment, and how they work to improve your heart’s function and quality of life.
What is Heart Failure?
Before we explore the CRT pacemaker, it’s important to understand heart failure. Heart failure occurs when the heart becomes weakened or stiff and can no longer pump blood effectively. It can happen for various reasons, including coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, valve disorders, and cardiomyopathy (a condition where the heart muscle becomes enlarged or weakened). This leads to a decrease in the amount of oxygenated blood being pumped to vital organs and tissues, resulting in a range of symptoms like:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and abdomen
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Difficulty exercising or doing everyday activities
Heart failure can be categorized into two main types: systolic and diastolic. Systolic heart failure occurs when the heart’s pumping function is weakened, and diastolic heart failure happens when the heart muscle becomes stiff and can’t relax enough to fill with blood properly.
Understanding CRT (Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy)
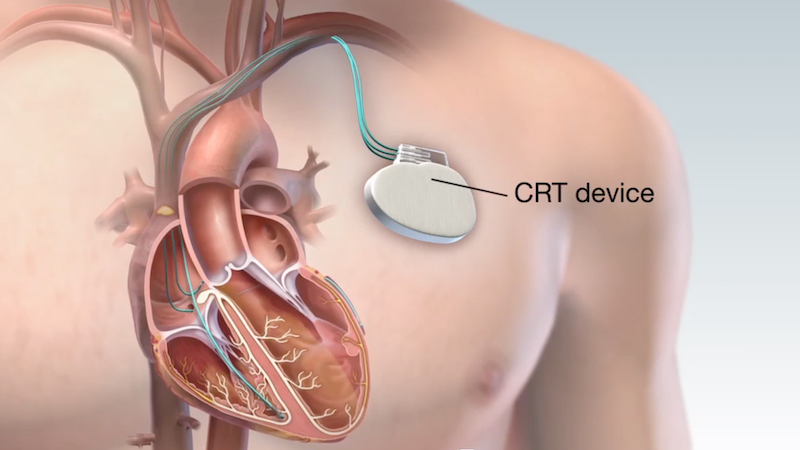
A CRT pacemaker is a device designed to improve the heart’s ability to pump blood by synchronizing the contractions of the heart’s chambers. It is specifically used for people with heart failure who have a condition called heart block or an irregular heart rhythm that prevents the left and right sides of the heart from beating in harmony.
Normally, the heart’s right and left ventricles contract together to pump blood to the lungs and the rest of the body. However, in some cases of heart failure, one side of the heart may beat too late, leading to inefficient pumping. This delayed contraction can significantly reduce the heart’s ability to pump blood and affect the heart’s overall function. A CRT pacemaker helps correct this problem by sending electrical signals to the heart to ensure that both ventricles contract at the same time, improving blood flow.
How Does a CRT Pacemaker Work?
A CRT pacemaker consists of a small device implanted under the skin, typically below the collarbone, and connected to the heart with wires (leads). The device delivers electrical pulses to the heart to help synchronize the heart’s contractions. Here’s how it works:
- Sensing the Heart’s Activity: The CRT pacemaker continuously monitors the heart’s electrical signals. If it detects that the heart’s contractions are out of sync, it sends electrical impulses to correct the timing.
- Synchronizing Heartbeat: When the device detects a delay between the left and right ventricles, it sends a signal to both ventricles to contract together. This improves the heart’s pumping efficiency and ensures that blood is delivered more effectively to the lungs and the rest of the body.
- Improving Heart Function: By coordinating the contractions of the heart, the CRT pacemaker helps the heart function more effectively. Over time, this can lead to an improvement in heart failure symptoms, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention.
Who is a Candidate for a CRT Pacemaker?
Not everyone with heart failure is a candidate for a CRT pacemaker. This treatment is most beneficial for people who meet the following criteria:
- Moderate to severe heart failure: CRT pacemakers are generally recommended for individuals who have moderate to severe heart failure (usually classified as NYHA class II, III, or IV).
- Reduced heart function: A CRT pacemaker is typically used for individuals with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 35% or lower. LVEF measures the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with each beat. An LVEF of 35% indicates significantly reduced heart function.
- Electrophysiological abnormalities: CRT is most effective in people with heart failure who also have an abnormality in the heart’s electrical conduction system, such as left bundle branch block (LBBB). In this condition, the electrical signals that control the heart’s beating are delayed, causing the heart’s chambers to contract out of sync.
- Symptomatic heart failure: Individuals who experience significant symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention, despite taking medications may benefit from CRT therapy.
Your cardiologist will assess your specific situation to determine whether you are a suitable candidate for a CRT pacemaker based on your heart failure symptoms, heart function, and the presence of electrical conduction abnormalities.
How a CRT Pacemaker Can Help Heart Failure
A CRT pacemaker can have several significant benefits for people with heart failure, particularly when combined with other treatments, such as medication and lifestyle changes. Let’s explore the key ways a CRT pacemaker can help:
1. Improved Heart Function
By synchronizing the heart’s contractions, a CRT pacemaker improves the efficiency of the heart’s pumping action. This can help reduce the strain on the heart and improve its ability to deliver oxygenated blood to the body. Over time, this can lead to an improvement in ejection fraction (the amount of blood the heart pumps with each beat), which is often reduced in heart failure patients.
2. Reduction in Heart Failure Symptoms
Many people with heart failure experience debilitating symptoms, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling. A CRT pacemaker can help alleviate these symptoms by improving the heart’s pumping ability, which can reduce fluid retention and improve exercise tolerance. Patients may notice they feel less fatigued, have more energy, and experience less difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
3. Reduced Hospitalizations
By improving heart function and reducing the severity of symptoms, a CRT pacemaker can decrease the number of hospitalizations related to heart failure. Studies have shown that CRT therapy can significantly reduce the risk of hospitalization and improve overall survival rates in heart failure patients.
4. Improved Quality of Life
Heart failure can drastically impact a person’s quality of life, making it difficult to perform everyday activities. By improving heart function and reducing symptoms, a CRT pacemaker can help patients return to normal daily activities, improving their overall well-being. Many people report feeling better physically, mentally, and emotionally after having a CRT pacemaker implanted.
5. Potential for Reverse Remodeling
One of the exciting aspects of CRT therapy is its potential to help reverse the structural changes that occur in the heart as a result of heart failure. Over time, the heart can become enlarged and weakened, a process known as cardiac remodeling. Studies have shown that CRT therapy can help reverse this remodeling, allowing the heart to regain its normal shape and function.
Risks and Considerations
While a CRT pacemaker can provide significant benefits, it is important to understand that there are some risks and considerations associated with the procedure:
- Surgical Risks: Implanting a CRT pacemaker requires surgery, and like any surgery, there are risks involved, including infection, bleeding, and complications from anesthesia.
- Device Malfunctions: As with any medical device, there is a small risk that the CRT pacemaker could malfunction, leading to inappropriate pacing or failure to deliver the necessary electrical signals.
- Lead Problems: The leads (wires) that connect the pacemaker to the heart can sometimes become dislodged, damaged, or infected, requiring additional procedures to correct the issue.
- Battery Life: CRT pacemakers are battery-powered devices, and the battery life typically lasts 5-7 years. When the battery begins to run low, the device will need to be replaced.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a CRT pacemaker?
A Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) pacemaker is a device used to help improve the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently in individuals with heart failure. It works by sending electrical impulses to both ventricles of the heart, helping them contract at the same time, which improves the synchronization of the heartbeat.
2. Who is a good candidate for a CRT pacemaker?
CRT pacemakers are typically recommended for individuals with moderate to severe heart failure, a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 35% or lower, and electrical conduction abnormalities such as left bundle branch block (LBBB). If you experience symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue despite taking medications, a CRT pacemaker may be a suitable treatment option.
3. How does a CRT pacemaker improve heart failure?
The CRT pacemaker improves heart failure by synchronizing the contractions of the heart’s ventricles. This helps the heart pump blood more efficiently, reduces symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath, and can improve overall heart function. Over time, it can also help reverse heart remodeling caused by heart failure.
4. What are the risks of getting a CRT pacemaker?
While a CRT pacemaker offers many benefits, there are risks associated with its implantation. These include surgical risks (infection, bleeding, anesthesia complications), device malfunction, lead problems (dislodgement or damage), and the need for battery replacement every 5-7 years.
5. How long does a CRT pacemaker last?
The battery of a CRT pacemaker typically lasts between 5 to 7 years. After this period, the device may need to be replaced or the battery replaced during a relatively simple procedure.
6. Can I still live a normal life after getting a CRT pacemaker?
Yes, many patients experience a significant improvement in their quality of life after getting a CRT pacemaker. Symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath may be reduced, and you may find it easier to perform daily activities and enjoy a more active lifestyle.
7. How do I know if a CRT pacemaker is right for me?
To determine if a CRT pacemaker is appropriate for your condition, your cardiologist will conduct an evaluation that may include tests like an echocardiogram, electrocardiogram (ECG), and other diagnostic assessments to assess your heart function and electrical activity.
Contact Details
Dr. Sanjeev Gera
MBBS, MD – Medicine, DNB – Cardiology
Cardiologist | 20 Years of Experience
Fortis Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences
Rasoolpur Nawada, Industrial Area, Sector 62, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301
Phone: +(91) 9810466173
Monday – Saturday | 8 AM – 5 PM
For any inquiries or to schedule a consultation, feel free to reach out to Dr. Sanjeev Gera’s office.