Introduction :
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk. In this blog, we will delve into the various aspects of heart disease, shedding light on its causes, common symptoms, and effective prevention strategies.
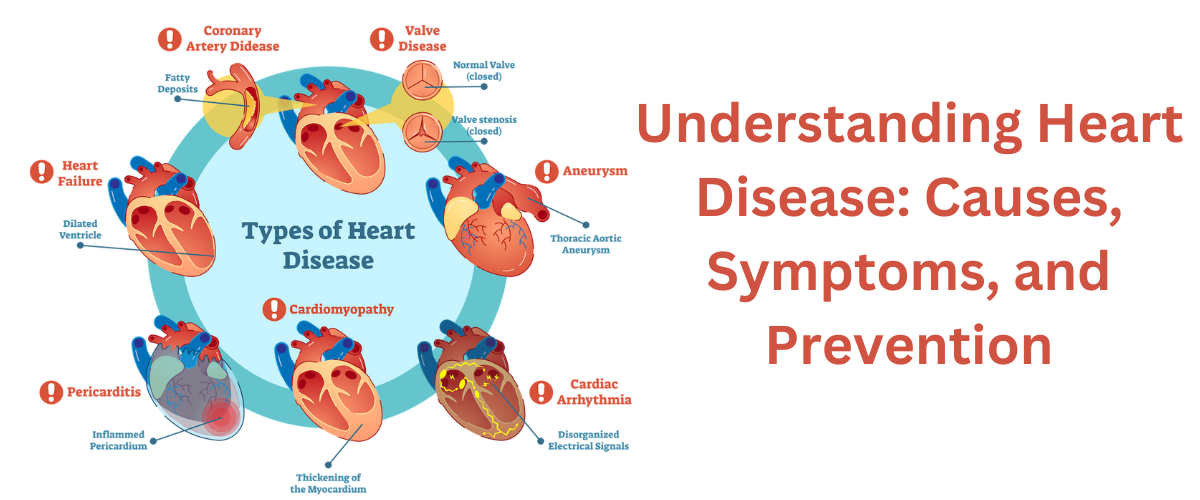
1. What is Heart Disease? :
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease, refers to a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. It encompasses various conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and valvular heart disease. These conditions can impede the heart’s ability to function properly and lead to severe health complications if left untreated.
2. Causes of Heart Disease :
Several factors contribute to the development of heart disease. The primary cause is the accumulation of fatty deposits, known as plaque, in the arteries, leading to a condition called atherosclerosis. This buildup restricts blood flow to the heart, causing it to work harder and potentially resulting in various heart-related issues.
Other risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, stress, and a family history of heart disease. Unhealthy dietary choices, such as consuming excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats, as well as refined sugars and salt, can also increase the risk.
3. Common Symptoms of Heart Disease :
Heart disease can manifest through various symptoms, which may vary depending on the specific condition. Common symptoms include chest pain or discomfort (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, rapid or irregular heartbeat, dizziness or lightheadedness, swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (edema), and persistent coughing or wheezing.
It’s important to note that some individuals may not experience any symptoms until the condition has progressed significantly. Therefore, regular check-ups and preventive screenings are crucial, especially for individuals with risk factors or a family history of heart disease.
4. Prevention Strategies :
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the risk of heart disease. Here are some effective strategies:
a) Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Adopt a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit salt, sugar, and processed food consumption. Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
b) Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol: Quit smoking, as it significantly increases the risk of heart disease. Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels.
c) Manage stress: Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy and relaxation.
d) Regular check-ups: Schedule routine visits with a healthcare professional to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular health.
e) Maintain a healthy weight: Aim for a healthy body weight and body mass index (BMI) by adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise.
Conclusion :
Understanding heart disease is crucial for its prevention and early detection. By knowing the causes, recognizing symptoms, and implementing preventive strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk and lead a heart-healthy life. Remember, small lifestyle changes can make a big difference in maintaining a strong and healthy heart.