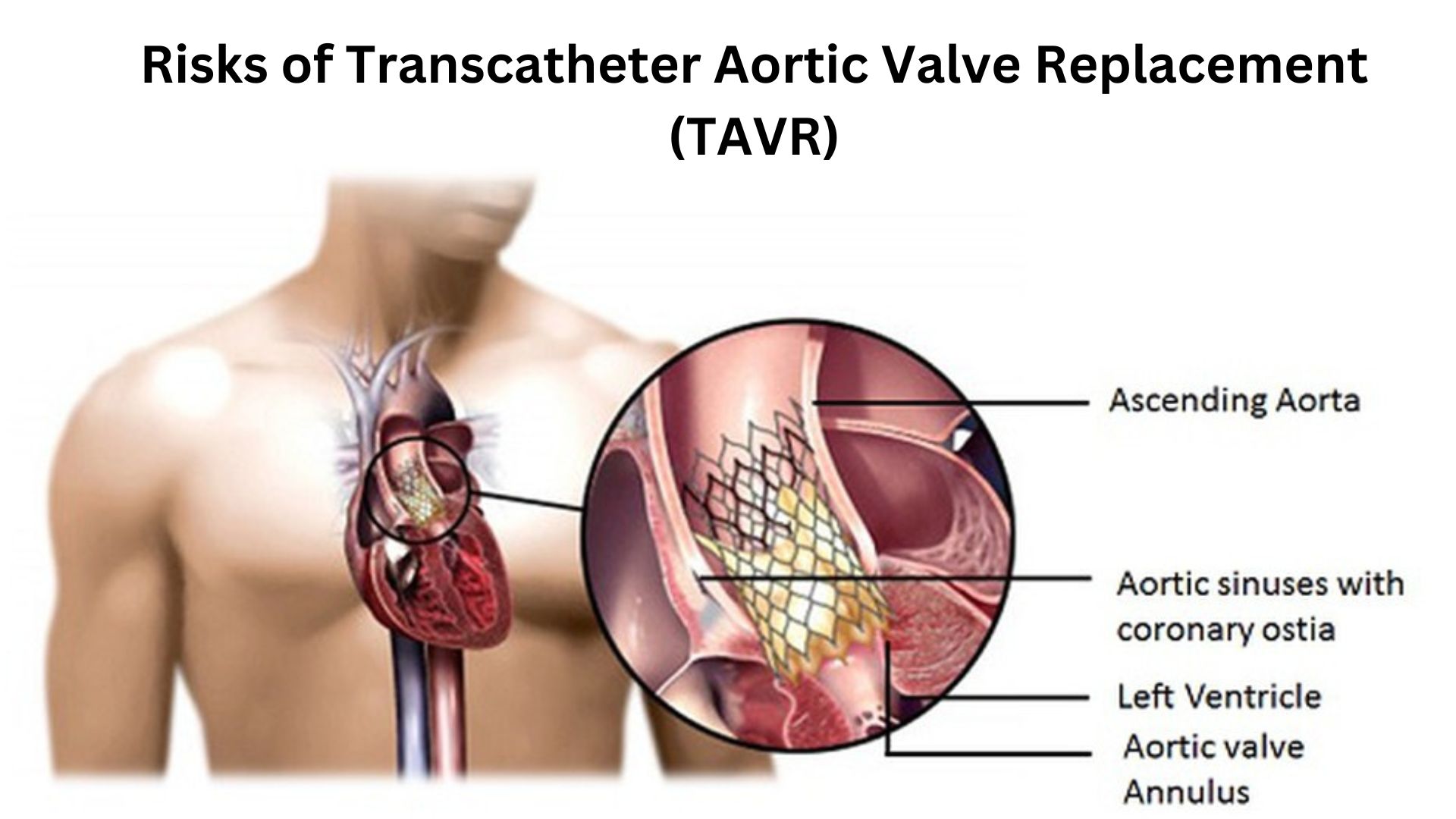
Understanding the Risks of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) is a groundbreaking procedure offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open-heart surgery for patients with severe aortic stenosis. While the benefits of TAVR are substantial, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks involved. Drawing insights from Stanford Health Care, let’s explore the key risks associated with TAVR to ensure you are well-informed.
Key Risks of TAVR
- Stroke
- Description: Stroke is a significant risk, occurring in a small percentage of patients undergoing TAVR.
- Cause: It can result from blood clots or debris dislodged during the procedure, which may travel to the brain.
- Impact: Strokes can lead to permanent neurological damage, requiring prompt medical attention and rehabilitation.
- Vascular Complications
- Description: Complications related to the blood vessels used to access the heart valve.
- Cause: These can arise from the insertion of the catheter, potentially causing damage to the arteries.
- Impact: Vascular complications may lead to bleeding, vessel injury, or the need for additional surgical intervention.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
- Description: A heart attack can occur during or after the TAVR procedure.
- Cause: It is often caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, possibly due to blockages or procedural manipulation.
- Impact: Immediate treatment is necessary to minimize damage and improve outcomes.
- Kidney Injury
- Description: Acute kidney injury is a potential risk, particularly in patients with pre-existing kidney issues.
- Cause: The use of contrast dye and changes in blood flow during the procedure can strain the kidneys.
- Impact: This condition may require dialysis and can affect overall recovery.
- Bleeding
- Description: Significant bleeding can occur at the catheter insertion site or within the body.
- Cause: Anticoagulant medications and procedural factors contribute to this risk.
- Impact: Managing bleeding is critical to prevent complications and ensure patient safety.
- Valve-Related Issues
- Description: Problems with the new valve, such as misplacement or leakage, may occur.
- Cause: These issues can arise from procedural errors or valve malfunctions.
- Impact: Valve-related complications may necessitate further surgical procedures to correct the problem.
Mitigating Risks
Healthcare providers take several measures to mitigate these risks, including:
- Pre-Procedure Assessment: Thorough evaluations to identify patients at higher risk for complications.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Utilizing precise imaging to guide the procedure and minimize errors.
- Experienced Surgical Teams: Ensuring that skilled and experienced professionals perform the TAVR procedure.
- Post-Procedure Monitoring: Close monitoring in the immediate post-procedure period to detect and address any complications promptly.
Conclusion
While TAVR presents a less invasive option for treating severe aortic stenosis, understanding and discussing the potential risks with your healthcare provider is essential. By being well-informed, you can make the best decision for your health, ensuring that the benefits of the procedure outweigh the potential risks.